The term “Fascisterne” is a Danish word that translates to “the fascists” in English. It refers to individuals, movements, or groups that embrace fascist ideology, an extreme right-wing and authoritarian political doctrine. Fascism has historically been associated with dictatorial regimes, ultranationalism, political repression, and racial superiority theories. In Danish society, as in much of the world, the term carries deeply negative connotations due to its direct link with some of the darkest chapters of the 20th century, such as Mussolini’s Italy and Hitler’s Nazi Germany.
While most often used in a historical context, the word “fascisterne” also appears in modern political debates, typically as a critical label directed at authoritarian or extremist right-wing movements.
What Does “Fascisterne” Mean?
The Danish word “fascisterne” is simply the plural form of fascist. It refers to groups or collectives that support fascist principles. These include:
- Strong authoritarian leadership: placing power in the hands of one dictator or ruling elite.
- Extreme nationalism: prioritizing the interests of one nation or ethnic group above others.
- Suppression of dissent: silencing political opponents, critics, and minority voices.
- Glorification of violence: often seeing war, militarism, and aggression as legitimate political tools.
In Denmark, as in other democratic societies, calling someone part of “fascisterne” implies strong condemnation. It is not a neutral term but one charged with political, social, and moral judgment.
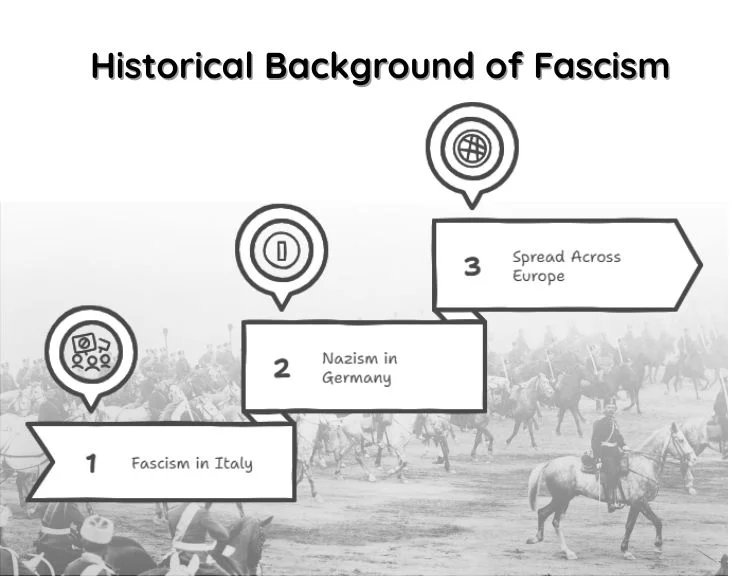
Historical Background of Fascism
To understand “fascisterne,” one must trace back to the roots of fascism in Europe during the early 20th century.
Fascism in Italy
- Founded by Benito Mussolini in 1919.
- Advocated corporatist economics, nationalism, and authoritarianism.
- Came to power in 1922, establishing a dictatorial regime.
Nazism in Germany
- Adolf Hitler’s Nazi Party took fascism further by combining it with racial ideology.
- Advocated Aryan superiority, anti-Semitism, and totalitarian rule.
- Led to the Second World War and the Holocaust, making fascism synonymous with genocide and oppression.
Spread Across Europe
- Fascist movements gained traction in Spain, Portugal, Hungary, and Romania.
- While not identical, they shared common principles of ultranationalism, militarism, and repression.
Thus, when Danes use the word “fascisterne,” it often recalls this shared European history of authoritarianism and destruction.
Fascisterne in Danish History
Although Denmark did not develop a large native fascist movement comparable to Italy or Germany, the country was affected by fascism during World War II.
- Denmark was occupied by Nazi Germany from 1940 to 1945.
- Danish collaborators and sympathizers with the Nazis were sometimes referred to as part of “fascisterne.”
- Resistance groups and democratic politicians used the word to distinguish themselves from occupiers and collaborators.
Even after the war, the term has remained a political insult and a warning against the dangers of authoritarian ideologies.
Characteristics of Fascisterne
To better understand the essence of “fascisterne,” it is useful to break down the core features of fascist groups and ideologies:
| Characteristic | Description |
| Authoritarian Leadership | Centralized power in one dictator or ruling elite. |
| Extreme Nationalism | Glorification of one nation, culture, or race above all others. |
| Suppression of Opposition | Elimination of political parties, media censorship, and silencing of dissent. |
| Militarism | Promotion of military values, violence, and war as tools of policy. |
| Propaganda Use | Heavy reliance on state-controlled propaganda to shape public opinion. |
| Racial/Cultural Superiority | Belief in hierarchy of races or cultures, often tied to discrimination. |
These traits define not only the fascist regimes of the past but also influence the way “fascisterne” is understood in modern discourse.
Fascisterne in Modern Political Discourse
Although classical fascism declined after 1945, the term “fascisterne” still appears in contemporary Danish and global debates.
- As a political accusation: used by democratic parties or activists to label authoritarian tendencies in opponents.
- Against far-right groups: applied to neo-Nazi organizations, white supremacists, and ultranationalists.
- In global politics: media sometimes uses it to describe leaders or governments that display dictatorial behavior.
However, scholars caution that overusing the term risks diluting its meaning. Not every authoritarian leader or right-wing group is fascist, though they may share similar traits.
The Negative Connotations of “Fascisterne”
In Danish society, the word “fascisterne” is a loaded term. Its strong negative associations come from:
- The Nazi occupation of Denmark, which remains a painful national memory.
- Fascism’s role in causing the Second World War and the Holocaust.
- Its contradiction with democratic values such as freedom, equality, and justice.
As a result, being called one of “fascisterne” is not only a political criticism but also a moral condemnation.
Why Fascism Still Matters Today
While fascism as a mass movement largely collapsed after 1945, elements of its ideology persist. Modern political analysts warn of neo-fascist tendencies in some groups that echo the past.
Key concerns include:
- Resurgence of extremist nationalism in Europe and beyond.
- Rising authoritarianism where leaders bypass democratic institutions.
- Hate speech, racism, and xenophobia gaining ground in some societies.
The term “fascisterne” is therefore used not only as a historical reference but also as a warning label in today’s world.
Conclusion
The Danish term “Fascisterne” carries a weight far greater than its simple translation of “the fascists.” It embodies the memory of an ideology that brought immense suffering to Europe and beyond. While originally tied to Mussolini’s Italy and Hitler’s Germany, it continues to resonate in modern discussions about authoritarianism, far-right extremism, and threats to democracy.
In Denmark, as in much of the world, “fascisterne” functions as both a historical reminder and a contemporary cautionary term. Its use underscores the importance of defending democratic values, protecting human rights, and remembering the dangers of totalitarian rule.






