Venezuela is a country on the northern coast of South America, officially known as the Bolivarian Republic of Venezuela. It is home to approximately 31.8 million people and is internationally recognized for having the world’s largest proven oil reserves. Venezuela’s diverse landscapes include towering mountains, vast plains, tropical rainforests, and iconic waterfalls, making it both geographically and culturally unique. This country is a vital member of OPEC, contributing significantly to the global oil market.
Its appeal extends beyond natural resources. Its rich history, vibrant culture, and ecological diversity attract both scholars and travelers. From the Andes Mountains in the west to the Amazon Basin in the south, and from the fertile Llanos to the majestic Angel Falls, the nation’s landscapes reflect centuries of natural evolution and human civilization.
History and Cultural Heritage
The independence movement, led by Simón Bolívar, played a critical role in freeing much of South America from colonial rule. The 19th and 20th centuries saw cycles of military governance and democratic reforms, shaping the modern Venezuelan state. Today, this culture reflects a fusion of Indigenous, Spanish, and African traditions, expressed in music, dance, cuisine, and literature.

Key cultural highlights include:
- Music: Joropo, salsa, and contemporary Venezuelan music.
- Cuisine: Arepas, hallacas, and tropical fruits.
- Festivals: Carnival celebrations, traditional dances, and regional fairs.
Population and Urban Centers
The population here is concentrated in the northern and western regions, with major urban hubs including Caracas, Maracaibo, Valencia, and Barquisimeto. These cities serve as centers for economic activity, culture, and education.
Urban life in Venezuela blends traditional and modern elements. While Caracas is the political and financial capital, other cities emphasize manufacturing, trade, and cultural heritage. The population is predominantly Christian, with Roman Catholicism being the most practiced religion, but indigenous and Afro-Venezuelan spiritual practices remain significant.
Geography and Natural Features
| Region | Key Features | Importance |
| Andes Mountains | Fertile valleys, high altitudes | Agriculture, tourism |
| Llanos | Grasslands, rivers | Livestock farming, biodiversity |
| Guiana Highlands | Tepuis, endemic flora & fauna | Scientific research, adventure |
| Amazon Basin | Rainforests, rivers | Biodiversity, conservation |
Economy and Oil Industry
Its economy is closely tied to its oil resources, which have historically driven national revenue and global influence. The country is known for having the largest proven oil reserves in the world, mainly concentrated in the Orinoco Belt. Oil revenue has shaped the nation’s economy, politics, and international standing.
Oil Reserves and Production
Venezuela holds approximately 303 billion barrels of proven oil reserves, giving it a leading position among OPEC members. The Orinoco Belt contains heavy crude oil that has attracted both national and foreign investment. Oil production remains central to government revenue and export earnings, despite recent declines in output.
OPEC Membership and Global Influence
As a founding member of OPEC, Venezuela plays a strategic role in global oil policy. Its production decisions impact international oil prices, energy markets, and geopolitical relations. Coordination with other OPEC countries ensures its continued relevance in the global energy sector.
Economic Diversification Efforts
While oil dominates the economy, it has significant opportunities to diversify. Initiatives focus on agriculture, mining, tourism, and renewable energy to reduce dependency on petroleum and stabilize long-term economic growth.
Challenges and Opportunities
The Venezuelan economy faces obstacles including infrastructure degradation, currency volatility, and international sanctions. Addressing these challenges is essential for attracting foreign investment and revitalizing domestic industries. Sustainable management of oil and non-oil resources is crucial for future prosperity.
Biodiversity and Environment
Environmental conservation is a priority, with national parks and protected areas safeguarding endemic species and natural landmarks. Canaima National Park and Mochima National Park are prime examples of ongoing preservation efforts.
Key environmental challenges:
- Oil spills and industrial pollution.
- Deforestation in the Amazon Basin.
- Pressures from tourism on delicate ecosystems.
Tourism and Travel Highlights
Venezuela offers ecotourism, adventure travel, and cultural experiences. Popular destinations include:
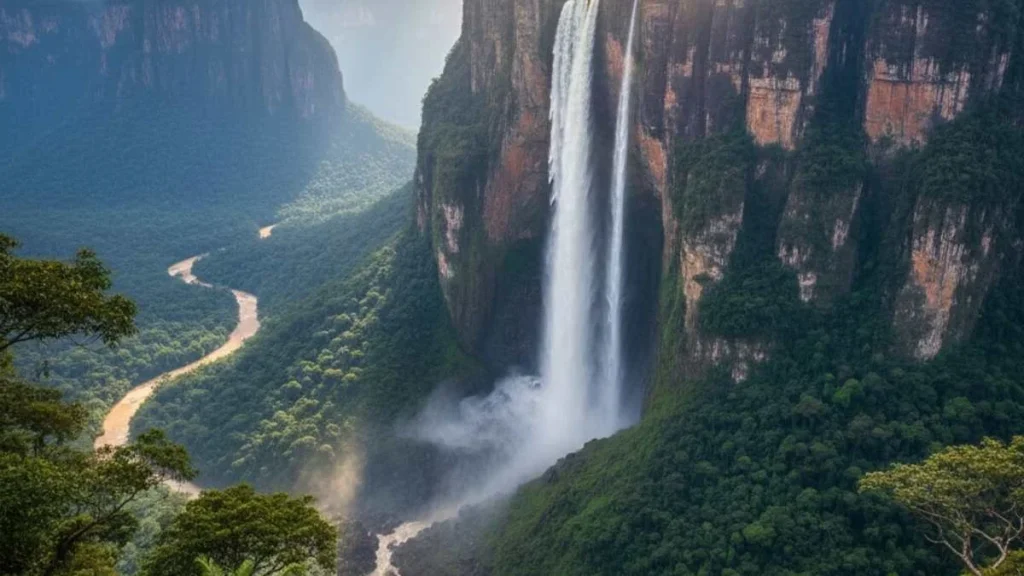

- Angel Falls: Highest waterfall globally.
- Los Roques Archipelago: Pristine beaches and coral reefs.
- Mérida Cable Car: Longest cableway in South America.
- Colonial towns: Historical architecture and traditional cuisine.
Infrastructure and Transportation
Venezuela’s infrastructure supports urban and rural connectivity. Major highways link Caracas with surrounding states, while airports like Simón Bolívar International Airport connect the country globally. Rail networks are limited but under gradual development, enhancing economic and tourism prospects.
Public transportation in cities includes buses, metro systems, and taxis. Investment in infrastructure is key to improving both domestic mobility and international trade.
Challenges and Development Opportunities
Despite its wealth, Venezuela faces political, economic, and social challenges. Economic diversification, infrastructure modernization, and environmental protection are critical for sustainable development.
Key opportunities include:
- Expanding ecotourism and cultural tourism.
- Investing in renewable energy sources.
- Strengthening agricultural production to reduce oil dependency.
- Promoting education and technology sectors for a skilled workforce.
FAQs
What is the official currency of Venezuela?
The Venezuelan Bolívar is the country’s official currency.
Which language is spoken in Venezuela besides Spanish?
Several indigenous languages, including Wayuu and Pemon, are spoken.
Is Venezuela safe for international tourists?
Tourist safety varies; research local conditions before traveling.
Conclusion
Venezuela is a nation of contrasts and possibilities. Its geography, from the Andes Mountains to the Amazon Basin, and its natural treasures like Angel Falls, position it as a globally significant country. Rich cultural heritage and indigenous traditions further enhance its global identity.
The future of it depends on harnessing its natural resources responsibly, addressing economic challenges, and protecting its environmental and cultural assets. With strategic planning, Venezuela can achieve sustainable growth while preserving the beauty and richness that make it truly unique.