Telemetryczny is a Polish adjective meaning “telemetric” in English. It refers to technologies, systems, or devices that collect, measure, and transmit data remotely for analysis or monitoring. In simple terms, anything telemetryczny relates to telemetry, the science of remote measurement and communication.
- Understanding the Concept and Origin
- How Telemetry Works in Simple Steps
- Key Fields Using Telemetryczny Systems
- Benefits of Adopting Telemetryczny Solutions
- Integration of Telemetry with Emerging Technologies
- Common Challenges and Limitations
- Telemetryczny Systems in Everyday Life
- Real-World Example of Telemetryczny Use
- FAQs
- Conclusion
In today’s connected world, telemetryczny systems power smart cars, satellites, hospitals, and IoT networks. They allow experts to gather real-time data from sensors located miles away, helping industries enhance efficiency, safety, and decision-making. Whether it’s tracking a rocket’s altitude, monitoring a patient’s heart rate, or optimizing factory operations, telemetryczny technology enables seamless, intelligent observation without physical presence.
Understanding the Concept and Origin
The word telemetryczny derives from telemetria, built from Greek roots tele (“remote”) and metron (“measure”). It describes processes that rely on sensors, transmitters, and receivers to collect and send measurements over distance.
A telemetryczny system may use radio waves, cellular data, or satellite networks to send information from a remote device to a central hub. This allows continuous monitoring of variables such as temperature, pressure, speed, or biological signals, making it invaluable in modern science and industry.
How Telemetry Works in Simple Steps
| Stage | Function | Example Application |
| 1. Data Capture | Sensors measure variables | Engine temperature sensor |
| 2. Signal Conversion | Converts analog to digital | Data acquisition module |
| 3. Transmission | Sends data via the network | Cellular, radio, or satellite |
| 4. Reception | The central system receives data | Cloud database |
| 5. Analysis | Algorithms interpret results | Predictive maintenance alerts |
Key Fields Using Telemetryczny Systems
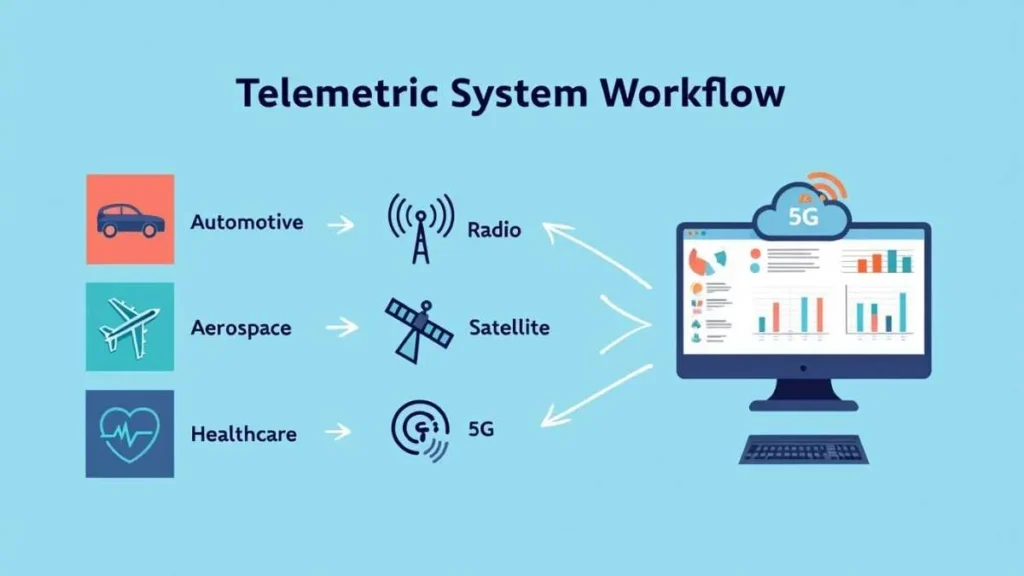
A. Automotive Industry
In the automotive world, telemetryczne systems are vital for performance optimization and safety. They collect real-time data on factors like fuel efficiency, engine temperature, and tire pressure. Racing teams depend on telemetry for instant adjustments during events, while everyday vehicles use it for diagnostics, navigation, and predictive maintenance, improving both reliability and environmental performance.
B. Aerospace and Aviation
Telemetryczny technology is indispensable in aviation and space exploration. Aircraft and spacecraft transmit continuous data on altitude, pressure, and system health to ground stations for analysis. This remote monitoring ensures flight safety and allows engineers to detect and fix issues before they escalate, keeping missions efficient and secure even across vast distances.
C. Medical and Healthcare
In healthcare, telemetryczny systems allow doctors to observe patients remotely through sensors tracking heart rate, oxygen levels, and temperature. Hospitals benefit from faster diagnosis and reduced emergency risks, while home monitoring helps patients manage chronic conditions safely under continuous supervision.
D. Internet of Things (IoT)
The IoT ecosystem depends on telemetry to connect devices and automate systems. From industrial machinery and smart homes to agriculture and energy grids, telemetryczny sensors transmit constant data for analysis. This enables predictive actions, energy savings, and smarter decision-making in connected environments.
Benefits of Adopting Telemetryczny Solutions
- Real-Time Visibility: Enables immediate insights into system performance.
- Operational Safety: Prevents failures before they escalate.
- Data-Driven Optimization: Improves resource use and planning.
- Remote Accessibility: Teams can monitor assets from anywhere.
- Cost Efficiency: Minimizes downtime and maintenance expenses.
Integration of Telemetry with Emerging Technologies
Modern telemetryczny frameworks leverage new-age innovations:
- 5G Connectivity: Ensures ultra-fast, low-latency data flow.
- Artificial Intelligence (AI): Interprets telemetry data for predictive analytics.
- Edge Computing: Processes information near the source to save bandwidth.
- Blockchain Security: Protects data integrity during transmission.
- Cloud Infrastructure: Offers scalable storage and analysis platforms.
Common Challenges and Limitations
Although telemetryczny systems offer immense advantages, they also face several challenges. Cybersecurity risks remain a major concern since continuous data transmission can expose systems to unauthorized access. Connectivity gaps in remote regions often hinder reliable signal flow, while data overload from massive sensor networks demands strong filtering and analysis tools. Integration complexity adds another layer of difficulty, as different devices and communication protocols must work together flawlessly.
Lastly, the cost of deployment, covering advanced sensors, hardware, and maintenance, can limit accessibility for smaller organizations. Overcoming these barriers requires enhanced encryption, robust network standards, and the growing use of AI-driven data management to secure and streamline telemetryczny operations.
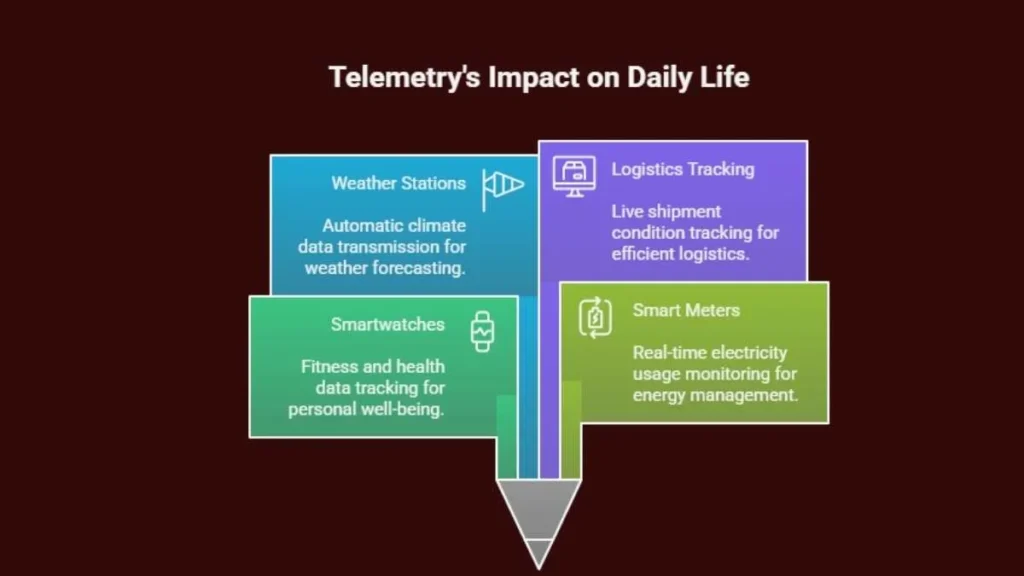
Telemetryczny Systems in Everyday Life
Even beyond industries, telemetry influences daily conveniences:
- Smartwatches record fitness and health data.
- Smart meters monitor electricity usage.
- Weather stations transmit climate readings automatically.
- Logistics companies track shipment conditions live.
Real-World Example of Telemetryczny Use
In electric vehicles (EVs), telemetry collects battery charge status, range data, and motor performance. This information is sent to cloud servers, where it helps manufacturers optimize software updates and maintenance schedules.
Similarly, in healthcare, a telemetryczny ECG monitor instantly alerts doctors to irregular heart rhythms, potentially saving lives. These examples highlight how telemetry bridges physical and digital worlds through intelligent, responsive data systems.
FAQs
Q1: How does telemetry differ from remote control?
A: Telemetry collects and sends data, while remote control sends commands back to the device.
Q2: What is a telemetryczny sensor used for?
A: It measures and transmits variables like temperature, speed, or pressure to a receiver.
Q3: Can telemetry work without the internet?
A: Yes, it can operate via radio, satellite, or local networks, depending on system design.
Conclusion
Telemetryczny technology represents the pulse of our data-driven era. By combining sensors, communication networks, and analytics, it delivers real-time insight that supports innovation across industries.
From medical monitoring to satellite communication, telemetry enables smarter, faster, and safer systems. As digital transformation accelerates, telemetryczny methods will continue empowering global progress, proving that distance no longer limits intelligence.






