Tribupneu is an advanced technological concept that merges tribology, the science of friction, wear, and lubrication, with pneumatic systems that operate using compressed air. It focuses on minimizing friction losses in air-driven mechanisms to improve performance, efficiency, and operational reliability across industrial and mechanical environments.
- The Scientific Foundation Behind This Innovation
- How the Integrated Approach Works
- Efficiency Gains and Operational Benefits
- Industrial Applications Across Sectors
- Comparison of Conventional vs Optimized Pneumatic Systems
- Emerging Use Cases Beyond Industry
- Contribution to Sustainable Engineering Goals
- Design Challenges and Engineering Considerations
- Future Outlook and Industry Adoption
- FAQs
- Conclusion
By applying tribological optimization to pneumatic components, this innovation enables smoother motion, precise control, reduced energy consumption, and extended equipment lifespan. Its relevance spans from sustainable industrial automation to the future development of air-assisted and respiratory technologies, making it a valuable advancement for high-performance and environmentally responsible engineering.
The Scientific Foundation Behind This Innovation
At Tribupneu’s core, this engineering concept is built on two well-established scientific disciplines that have traditionally evolved independently. Their convergence creates a system-level advantage that addresses long-standing inefficiencies in mechanical operations.
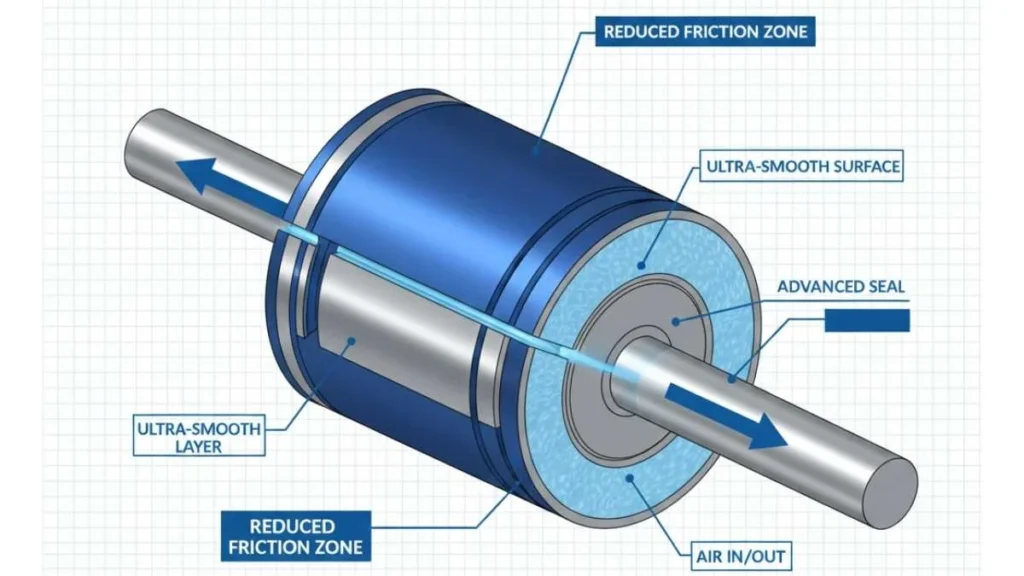
Tribology examines how interacting surfaces behave under motion and load. Friction and wear are unavoidable in mechanical systems, but when unmanaged, they cause excessive energy loss, heat buildup, and premature failure of components. Engineers apply surface treatments, specialized coatings, and optimized lubrication to control these effects.
Pneumatics use compressed air to generate mechanical movement. These systems are valued for their safety, cleanliness, rapid response, and adaptability. They are widely used in manufacturing lines, automation, packaging, food processing, and medical equipment.
How the Integrated Approach Works
By applying friction-reduction principles directly to pneumatic components, Tribupneu transforms how air-powered systems perform. It is not a single product or device but a design philosophy that influences materials, surface finishes, and lubrication strategies across the system. Key Engineering Enhancements
- Optimized surface roughness for reduced resistance
- Advanced low-friction coatings on moving parts
- Precision lubrication tailored for air-driven environments
- Improved seal design to minimize air leakage
These refinements allow pneumatic systems to operate more smoothly while consuming less energy.
Efficiency Gains and Operational Benefits
Improved Energy Utilization
Compressed air generation is energy-intensive. Any friction-related loss forces compressors to work harder, increasing electricity consumption. By minimizing internal resistance, this technology reduces the required air pressure for the same output.
As a result, industries experience lower operational costs and improved sustainability metrics without sacrificing performance.
Enhanced Precision and Motion Control
In automated environments, even minor inconsistencies can disrupt workflows. Friction-related hesitation or vibration often leads to positioning errors or delayed responses.
Smoother surface interaction ensures consistent motion, faster response times, and higher repeatability, critical for robotics, assembly lines, and precision handling tasks.
Lower Maintenance and Downtime
Wear-related failures are a major cause of production interruptions. Reducing surface degradation extends component life and decreases the frequency of inspections and replacements.
Industrial Applications Across Sectors
Smart and Sustainable Manufacturing
Modern production facilities like Tribupneu aim to balance productivity with environmental responsibility. Pneumatic systems already offer cleaner operation compared to hydraulic alternatives. When enhanced through friction optimization, they become even more energy-efficient.
This supports eco-friendly manufacturing goals while maintaining high throughput and reliability.
Automation and Robotics Systems
Air-powered actuators are widely used in robotic arms, gripping systems, and material transfer units. Reduced resistance improves control accuracy and operational safety.
This is especially important in collaborative automation environments where machines interact closely with human operators.
Process, Packaging, and Handling Industries
Industries such as food processing, pharmaceuticals, and packaging rely on clean, contamination-free systems. Optimized pneumatic components help maintain hygiene standards while improving system longevity and throughput consistency.
Comparison of Conventional vs Optimized Pneumatic Systems
| Feature | Conventional Pneumatics | Optimized Air Systems (Tribupneu) |
| Friction Loss | High | Significantly Reduced |
| Energy Consumption | Higher | Lower |
| Component Wear | Faster | Slower |
| Motion Precision | Moderate | High |
| Maintenance Frequency | Frequent | Reduced |
Emerging Use Cases Beyond Industry
Air-assisted medical devices require precise airflow and dependable operation. Applying tribological principles enhances performance consistency while reducing noise and mechanical stress.
In aerospace testing, laboratory automation, and advanced prototyping, stable and predictable system behavior is essential. Optimized pneumatic designs support high-accuracy experimentation and controlled environments.
Contribution to Sustainable Engineering Goals
Sustainability is increasingly central to engineering decisions. By lowering energy demands and extending equipment lifespan, this approach directly contributes to reduced emissions and resource consumption.
Longer service life also means fewer replacements, lowering material waste and manufacturing impact over time.
Design Challenges and Engineering Considerations
Implementing this system-level optimization requires multidisciplinary expertise. Engineers must carefully select materials, coatings, and lubricants compatible with compressed air environments.

While initial development costs may be higher, lifecycle savings and performance improvements typically justify the investment.
Future Outlook and Industry Adoption
As materials science advances and smart manufacturing expands, this integrated approach is expected to become a standard design consideration for pneumatic systems.
Future developments in Tribupneu may include adaptive surface technologies and real-time monitoring for friction management, further enhancing efficiency and reliability.
FAQs
Q1. Can Tribupneu reduce compressed air costs?
Yes, by minimizing friction losses, it lowers the air pressure and energy required for operation.
Q2. Is Tribupneu suitable for cleanroom environments?
Yes, optimized pneumatic systems are compatible with contamination-sensitive applications.
Q3. Does Tribupneu require redesigning entire systems?
Not always; improvements can often be integrated into existing pneumatic components.
Conclusion
This advanced integration of friction science with air-powered mechanics in Tribupneu represents a meaningful shift in how pneumatic systems are designed and optimized. Addressing efficiency losses at their root enables smoother operation, reduced energy consumption, and longer-lasting components.
As industries continue to prioritize sustainability, automation, and precision, this innovation offers a practical pathway to achieving those goals. Its growing relevance across manufacturing, healthcare, and advanced engineering positions it as a key contributor to the next generation of high-performance air-driven systems.