Hormita is a comprehensive lifestyle philosophy that promotes sustainability, balance, and mindful consumption as a unified way of living. It focuses on aligning human behavior with environmental responsibility, emotional well-being, and conscious decision-making. Rather than being a trend, it represents a long-term value system that guides how individuals interact with nature, society, and resources in everyday life.
- The Foundations of Hormita Philosophy
- Living in Harmony with the Environment
- Sustainable Living Practices
- Fostering Community Connections
- Building Personal and Collective Resilience
- Mindful Consumption Culture
- Psychological and Emotional Well-Being
- Everyday Life Integration
- Comparison of Traditional Living vs Conscious Living
- Long-Term Cultural Transformation
- Future Vision of Conscious Living
- FAQs
- Conclusion
Hormita emphasizes harmony with the environment, strong community connections, and long-term resilience. It supports ethical living, ecological awareness, and intentional choices that create stability for both individuals and societies. By integrating sustainability with mental clarity and social responsibility, it offers a structured approach to modern living that is both practical and purpose-driven.
The Foundations of Hormita Philosophy
The philosophy is structured around three integrated principles that guide daily life and long-term behavior. These foundations shape how people consume, interact, and grow within their environments.
Sustainability represents responsible use of natural resources, environmental preservation, and regenerative thinking. Balance supports physical, emotional, and mental stability through healthy routines and conscious priorities. Mindful consumption focuses on intentional ownership, ethical sourcing, and long-term value rather than excess.
Together, these elements form a coherent lifestyle system that supports human well-being and planetary health simultaneously.
Living in Harmony with the Environment
Environmental harmony is a central pillar of this lifestyle model. Humans are viewed as part of natural systems rather than separate from them. Ecological responsibility becomes a daily practice instead of a distant goal.
This includes protecting biodiversity, preserving natural ecosystems, reducing pollution, and supporting sustainable development practices. The philosophy encourages long-term thinking, where decisions are evaluated based on their future impact rather than short-term convenience.
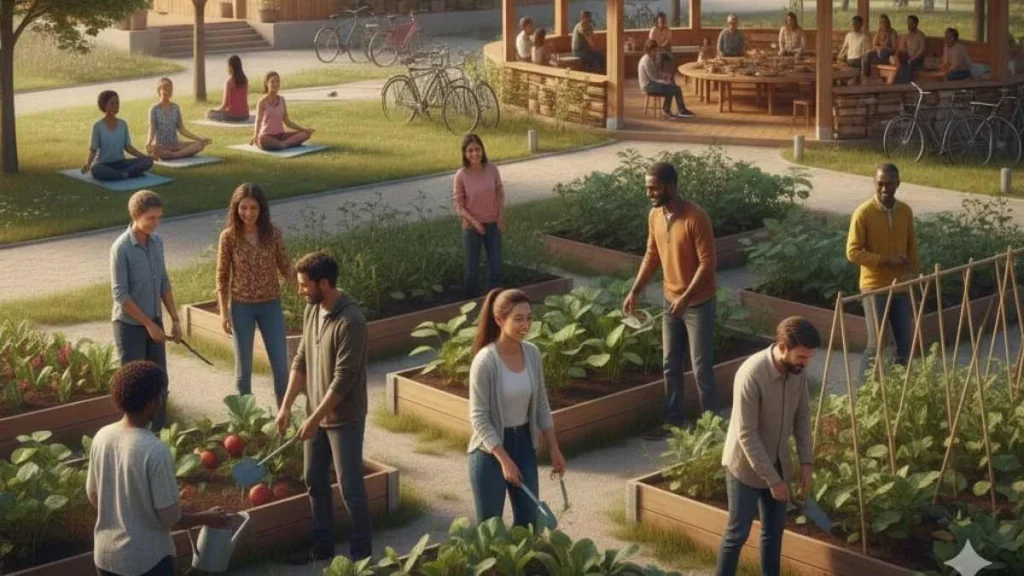

Sustainable living becomes a behavioral standard rather than a symbolic action, shaping housing choices, food systems, transportation habits, and energy use patterns.
Sustainable Living Practices
Sustainability is expressed through practical daily actions that reduce environmental impact while improving quality of life. These practices integrate seamlessly into routines without creating lifestyle pressure.
Examples of sustainable habits include:
- Low-waste living and recycling systems
- Energy-efficient housing and renewable energy usage
- Sustainable food sourcing and reduced food waste
- Eco-conscious transportation methods
- Ethical fashion and responsible manufacturing choices
These habits promote long-term environmental stability while supporting personal well-being and economic efficiency.
Fostering Community Connections
Community as a Support System
Strong communities create trust, shared responsibility, and collective growth, providing emotional security and resilience.
Local Collaboration
Encouraging neighborhood initiatives, cooperative economies, and mutual aid strengthens social infrastructure and reduces reliance on fragile centralized systems.
Knowledge and Resource Sharing
Sharing skills, resources, and knowledge fosters stronger bonds and sustainable community development.
Emotional and Social Well-being
Community involvement improves mental health, builds trust, and encourages empathy, creating a more harmonious society.
Building Personal and Collective Resilience
Resilience is developed through adaptability, emotional intelligence, and long-term planning. It applies to individuals, communities, and systems.
Collective resilience focuses on strong local economies, decentralized systems, and adaptable infrastructures. Communities that invest in cooperation and sustainability are better prepared for economic shifts, climate risks, and social disruptions.
Mindful Consumption Culture
Key aspects of mindful consumption include:
- Prioritizing quality over quantity
- Choosing ethical and sustainable products
- Reflecting personal values in purchasing decisions
- Reducing financial waste through intentional spending
- Minimizing the environmental impact of daily consumption
Psychological and Emotional Well-Being
By reducing excess, distraction, and overstimulation, individuals experience improved focus, emotional balance, and psychological stability. Life becomes less reactive and more intentional.
Identity alignment also improves, as personal values, actions, and beliefs remain consistent, reducing stress and internal conflict.
Everyday Life Integration
Daily integration includes sustainable choices, meaningful relationships, mindful routines, and ethical decision-making. Small actions accumulate into long-term transformation.

Lifestyle change becomes natural, gradual, and sustainable rather than forced or extreme.
Comparison of Traditional Living vs Conscious Living
| Aspect | Traditional Lifestyle Model | Conscious Lifestyle Model |
| Consumption | Excess-driven | Value-driven |
| Community | Individual-centered | Community-centered |
| Resources | Exploitative use | Regenerative use |
| Success | Material growth | Sustainable well-being |
| Stability | Short-term comfort | Long-term resilience |
Long-Term Cultural Transformation
Hormita represents a cultural evolution rather than a lifestyle trend. It shifts societal priorities from unlimited growth to sustainable development.
Human progress becomes defined by regeneration, stability, and well-being instead of consumption and speed. Interdependence replaces isolation, and collective success replaces individual excess.
This cultural transformation supports long-term planetary health and social stability.
Future Vision of Conscious Living
As environmental challenges grow and social systems evolve, this philosophy offers a flexible framework for future living.
It adapts across cultures, economies, and communities because it is principle-based rather than rigid. Progress, responsibility, and awareness guide transformation rather than perfection.
This approach creates a stable foundation for future generations to thrive within ecological limits.
FAQs
Is Hormita suitable for urban living?
Yes, it adapts easily to both urban and rural environments.
Does Hormita require major lifestyle changes?
No, it promotes gradual, sustainable improvements.
Can businesses adopt Hormita?
Yes, organizations can integrate them into ethical and sustainable business models.
Conclusion
Hormita offers a structured, ethical, and sustainable approach to modern living. It integrates environmental responsibility, personal well-being, and social resilience into one unified system. Living consciously becomes both a personal and collective responsibility.
By aligning values with actions, Hormita transforms daily life into purposeful living, consumption into responsibility, and community into strength. It provides a realistic, long-term framework for human flourishing rooted in balance, sustainability, and mindful awareness.